Human Pre-History and the Making of the Races, Part 1
Since the 1950 UNESCO Statement on Race there has been an increasing tendency to claim, based on Boasian anthropology and in promotion of a multiracialist agenda, that the human races are “socially constructed” and their existence is not supported by science, meaning not biologically and genetically real. This essay is an account, consistent with current scientific knowledge, of how the human races we know historically and today were really constructed.
The human species is blessed with great variety and diversity. Its rich diversity resulted from its global distribution, which caused the different populations of humanity to be geographically separated and thus reproductively isolated. Reproductive isolation enabled divergence — the process of divergent evolution — to occur, causing the isolated populations to evolve in different directions, developing their own distinct ensembles of genetic traits and characteristics.
Divergent evolution is the process by which new life forms are created by the division and separation of life into different branches. Human evolution has seen its share of divergent branching. The generic name commonly used to refer to the genetically different populations—that share a common biological ancestry that distinguishes them from other populations — is race. But in the human species, as in any species enjoying a great degree of variety, the constant branching and dividing that characterize the process of divergent evolution have created many different divisions, each of which possesses a genetic signature which distinguishes it from other divisions at the same level. For purposes of taxonomic accuracy each of these levels should have its own specific name and definition. The first or highest level is the species, and it is simply and objectively defined as including all those populations which are capable of interbreeding with each other and producing fully fertile offspring. The term race is commonly used to refer to a branch or division of the species possessing genetically transmitted physical traits (e.g., skin color) which distinguish it from other branches or divisions of the same level. Adding to this definition, it will here also be defined as including only those persons who are capable of reproduction with each other without alteration of the racially-distinctive genetic traits of either parent stock; that is, the genetically transmitted traits which distinguish a race from other divisions at the same level (i.e., other races) should not be diminished or lost by reproduction within the race. If racially-distinctive traits are lost or diminished by within-group reproduction then the population group is at a level of division too broad and inclusive to be accurately defined as a race. If it is too narrow to be defined as a species, as it does not include all those populations capable of interbreeding, then it is at a level between race and species, which will here be referred to as a subspecies.
The closest living relative of humanity—the still existing species most closely related to Homo sapiens—is the Chimpanzee, whose ancestral line branched from the line leading to humans about 5.5 million years ago. Even after 5.5 million years of divergent evolution humans and chimpanzees still have over 98% of their genes in common, with only a 1.23–1.6% difference in their genome. The genus Homo originated with Homo habilis in the region of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya and Ethiopia in east Africa about two million years ago, where it continued to evolve, first as Homo ergaster and Homo erectus, then as Homo antecessor (750,000 years ago) and Homo heidelbergensis (600,000-250,000 years ago; believed to be the direct ancestor of Homo neanderthalensis in western Eurasia), and then as Homo sapiens idaltu, the earliest modern humans, with finds in Ethiopia dated to 195,000 and 160,000 years ago (Scientific American 16, no. 2, 2006, p. 78).
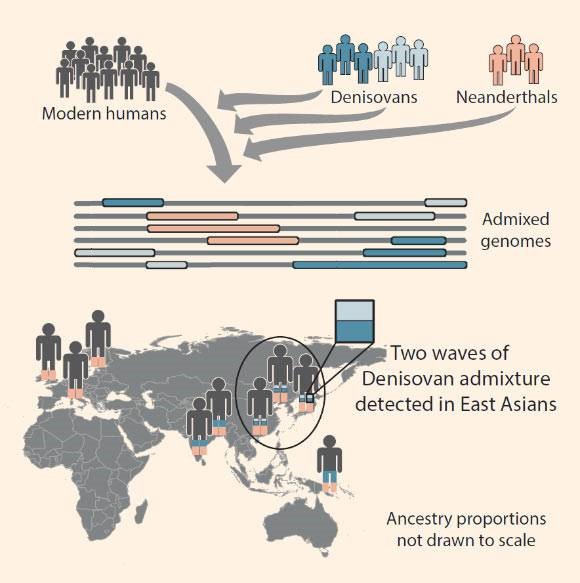
The current (2019) general consensus is that there were at least three major migrations or expansions of the genus Homo out of east Africa into Eurasia, either crossing the Sinai peninsula from Egypt into the Levant (the coast of what is now Israel, Lebanon and Syria), or crossing the southern entrance of the Red Sea (the Bab el Mandeb) from Djibouti in Africa to Yemen in Asia, from where they spread throughout most of Eurasia and developed into a variety of regional “archaic” human populations. The first of these major expansions out of east Africa into Eurasia was about 1.8 million years ago, the second about 600,000 years ago (associated with the spread of the Acheulean culture), and the last shortly after 100,000 years ago. Beginning in 1987, based on genetic studies showing that the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and the Y-chromosome of all living humans is derived from the last of these major expansions, the common view expressed in the popular press (called “Out-of-Africa”) has been that the modern humans of the final migration completely replaced the regional archaic human populations from the first two major expansions. But beginning circa 2002 genetic studies by Alan Templeton and others have increasingly supported the view (called “Out-of-Africa-Again-and-Again”) that although all our surviving mtDNA and Y-chromosome lineages as well as the majority of our other genes derive from the most recent expansion, a significant minority of our other genes have much older “coalescence” dates and must therefore derive from the regional archaic human populations of the first two major expansions. These studies indicate that some genes from the regional populations of the first expansion were assimilated and perpetuated by the populations of the second expansion, and that some of the genes of both of the first two (archaic) expansions were assimilated by the modern humans of the final expansion.
The first dispersal of modern humans probably began soon after the emergence of Homo sapiens idaltu in east Africa about 195,000 years ago, with some populations heading west into the tropical forest of the Congo basin where they intermixed with local archaic elements and evolved into the Congoid subspecies, others remaining in east Africa where they evolved into the Capoid or Khoisanid (San-Bushmen) subspecies, and others moving north to the shores of the Red Sea, where they became the progenitors of the population that eventually migrated out of Africa and populated the rest of the world, intermixing with regional archaic human populations they encountered in varying degrees, and evolving into the Australoid, Mongoloid and Caucasoid subspecies. By 130,000 years ago there were perhaps 10,000 modern humans living in different populations in different regions of Africa. About 120,000 years ago one of these modern human populations that had expanded up the Nile valley crossed the Sinai peninsula out of Africa into the Levant but no traces have been found of them after 90,000 years ago.
The final major expansion out of east Africa into Eurasia, perhaps numbering only a few hundred people at the beginning, crossed from northeast Africa to southwest Asia after 90,000 years ago, where they engaged in some intermixture with the local archaic Neanderthal groups. The descendants of this population gradually expanded and dispersed, with the initial expansion being along the southern coast of Asia. The where and when of these early human migrations was largely determined by geography, especially changes in climate and sea level. The first main split or division in the expansion occurred when some groups continued to move east while others remained in southwest Asia. The second main branching or division probably occurred after the eastward migrating group reached southeast Asia and intermixed with local archaic Denisovan elements, with one branch continuing to move eastward, reaching southern China by 68,000 years ago, where it experienced additional archaic Denisovan intermixture, and another branch remaining in the Burma-Thailand region, where it evolved into a proto-Australoid population, then expanded south through Malaysia and Indonesia, reaching New Guinea by 77,000 years ago and Australia by 65,000 years ago.
The eruption, or explosion, of the Toba super-volcano in northern Sumatra circa 74,000 years ago, the largest such explosion in the last two million years, perhaps 100 times larger than the Krakatoa event off southern Sumatra in 1883, covered the entire Indian sub-continent in several meters of ash, probably destroying almost all life, including the early human population in the area. The populations to the east and south of the eruption were spared its catastrophic effects, but the population in southwest Asia, and to a lesser extent the population in east Africa, probably suffered severe climate effects. The population in west Africa, protected by mountains to the east, was not as seriously affected. Within a few thousand years India was repopulated from the east by proto-Australoids.
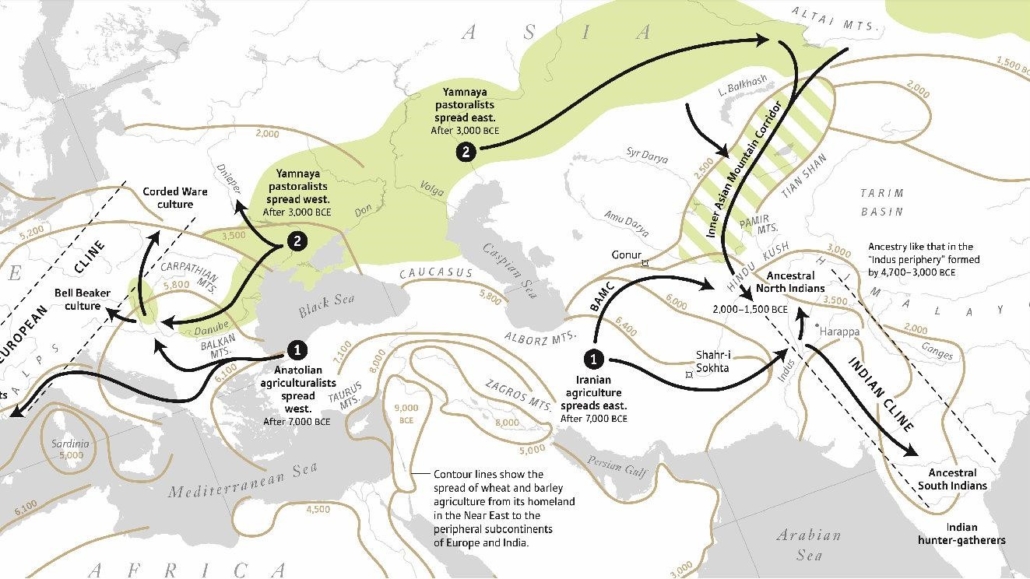
By 50,000 years ago the population that had remained in southwest Asia had evolved into proto-Caucasoids and began to expand: to the northwest up the Tigris-Euphrates valley to the Levant by 45,000 years ago; and to the northeast through Central Asia to the mammoth steppe of Siberia where they developed into the Ancient North Eurasians. From the Levant they expanded north into Anatolia, from there entering Europe through the Balkans and spreading the Aurignacian culture across southern Europe by 43,000 years ago. From the steppes of Siberia they moved westward into Europe, spreading the Gravettian culture, about 33,500 years ago. Shortly after this another Caucasoid group expanded from the Levant across North Africa. In this same time frame the population in Indochina and southern China had evolved into proto-Mongoloids and expanded northwards into the steppes of eastern Siberia, branching into southern and northern Mongoloid groups. Some of the northern proto-Mongoloids in eastern Siberia intermixed with Ancient North Eurasian Caucasoids and subsequently migrated east across the Beringia land bridge, from where they moved south into the Americas.xxxxx
By 30,000 years ago the divergent evolutionary branching of the human species had produced five main lines or subspecies which are still extant: the Congoid of West and Central Africa; the Capoid of East and South Africa (later replaced in East Africa by the Congoid); the Australoid of India, Burma, Malaya, Indonesia, New Guinea and Australia; the Mongoloid of East Asia (later expanding to the southwest into Burma, Malaya and Indonesia, largely replacing the indigenous Australoids) and the Caucasoid of Europe, North Africa and West Asia. These subspecies branched or divided in turn into separate races, and these races branched in their turn into subraces, as part of the continuing process of divergent evolution.
Beginning about 20,000 years ago, when the global human population was perhaps a million, the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) pushed the population of northern Europe south to refuge areas (refugia) in southern France, northern Spain, the Balkans and Ukraine, while the now fully-developed northern Mongoloid population in Siberia was also forced south to eastern and southern China. Both populations were greatly reduced in number during this period. When the Last Glacial Maximum began to recede about 15,000 years ago (13,000 B.C.) the survivors of these populations expanded northward again from their refuge areas, with Scandinavia and Britain being occupied about 11,000 years ago, by which time the global human population had risen to perhaps 10 million.
Agriculture and the Neolithic (New Stone Age) period began about 12,000 years ago in southwest Asia and shortly after in China. Prior to this all the populations of humanity had always been “hunter-gatherers,” living by hunting and gathering the fruits of the natural vegetation, which could only support a low-density population. Agriculture supported a much higher population density than hunter-gathering, and so enabled massive population growth which spurred geographic expansion and the replacement of hunter-gatherer peoples by Neolithic farmers in varying degrees. Over the course of many generations the Mongoloid rice farmers of southern China expanded southwards into southeast Asia and across Indonesia, mixing with, assimilating and largely replacing the smaller aboriginal populations of Australoid hunter-gatherers. Similarly, the Caucasoid wheat farmers of southwest Asia expanded eastward into Pakistan and northern India, where they mixed with and partly replaced the native Australoid hunter-gatherers, westward across North Africa, and northwest into Anatolia. Starting about 8,500 years ago (circa 6,500 BC) they crossed from Anatolia across Europe, mixing with, assimilating and largely replacing the indigenous Caucasoid hunter-gatherer populations in the south, less so in the north. This expansion had two branches, the first moving through the Balkans and up the Danube valley into central and northern Europe, the other moving through the Mediterranean to the Iberian peninsula and then north through western Europe, reaching the British Isles about 6,000 years ago (circa 4,000 BC); it is noted for creating megalithic structures such as Stonehenge (circa 2,500 BC).
The last major demographic and genetic shift in the Caucasoid region started about 5,200 years ago (circa 3,200 BC) with the expansions of what is currently (2019) referred to as the Yamnaya peoples of the Pontic-Caspian steppe, centered in what is now Ukraine. The Yamna are also known as the Kurgan people, with both terms derived from their custom of burying their dead in pit graves (local word “yama” for pit) under mounds or tumuli of earth (local word “kurgan” for mound or barrow). The Yamna-Kurgans, largely descended from the Ancient North Eurasians, were a semi-nomadic pastoral people who herded cattle and sheep on the steppe and domesticated the horse for use in herding and war. They were also the source and carriers of the Indo-European languages which they spread with their conquests and genes. By 2,600 BC the peoples of the “Corded Ware” (named after the style of their ceramic ware or pottery) aka “Battle-Axe” cultural “horizon” across north-central and northeastern Europe were genetically over 75 percent Yamna-Kurgan in ancestry, largely replacing the earlier mixture of hunter-gatherer and Neolithic farmer elements.
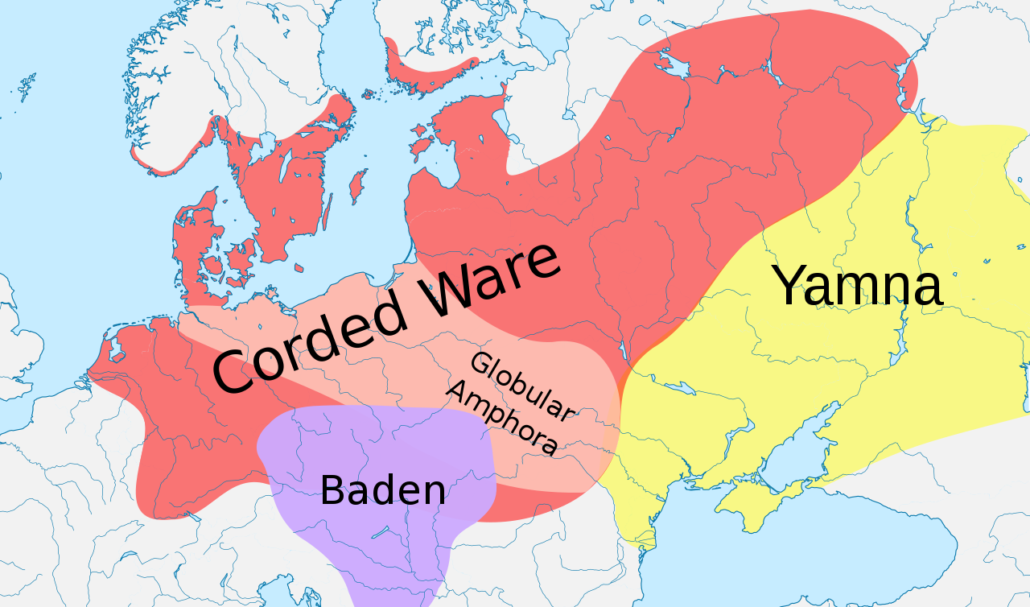
After 2,500 BC the predominantly Yamna-Kurgan elements of the Corded Ware culture blended with the peoples of the expanding “Bell Beaker” culture (also named after the style of their pottery) of western and central Europe and with this culture expanded into the British Isles, again largely replacing the existing population.
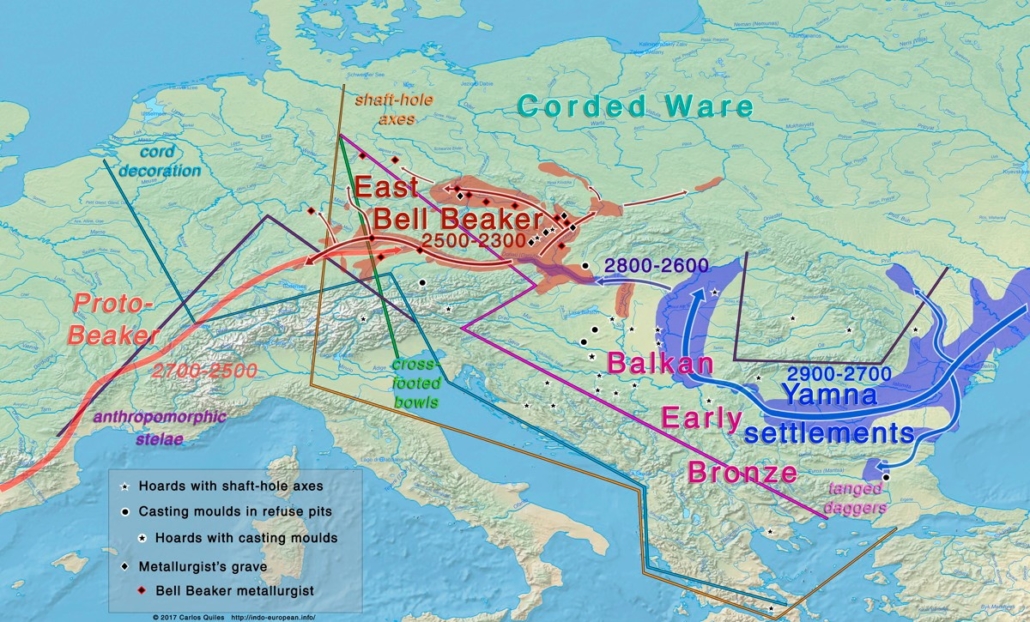
By 2,000 BC the steppe descendants of the Yamna-Kurgans had expanded as far east as the Tarim basin of northwest China, where their tartan-clad blond and red-haired mummified remains have been found. After 2,000 BC, under the name Aryans, they expanded southeast into Iran, Pakistan and northern India, where they brought Indo-European languages including Persian and Sanskrit, and in the latter case gradually blended with a much larger mixed Caucasoid and Australoid population. During the same period, they also expanded southwest from the steppe through the Caucasus into Anatolia and through the Balkans to Greece, where they later formed the ruling elements of the Hittite and Mycenaean civilizations.
To this day Yamna-Kurgan ancestry accounts for over 50 percent of genetic ancestry in Scandinavia, Finland and the Baltic states, 48 percent in Scotland and 41 percent in England. It declines moving south, to 38 percent in France, 28 percent in Tuscany (central Italy), 23 percent in Spain, 20 percent in Greece and 5 percent in Sardinia. Neolithic farmer ancestry tends to follow the opposite pattern, declining toward the north from 88 percent in Sardinia to 76 percent in Spain, 72 percent in Tuscany, 51 percent in France, 43 percent in England, and under 30 percent in Scotland and Norway. The more varied hunter-gatherer component (see below) is largest in the northeast (e.g., Estonia at 37 percent, Lithuania 32 percent, Belarus and Ukraine 28 percent) and the more remote areas of the northwest (e.g., the Orkney islands at 27 percent and Scotland at 23 percent) where there was less Neolithic farmer penetration.
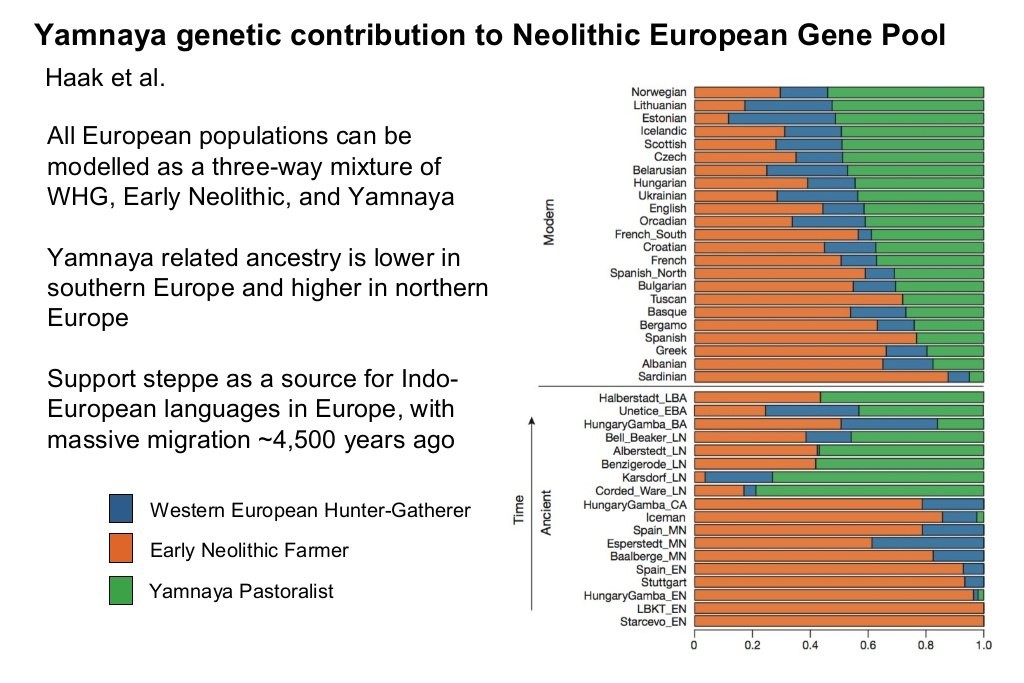
The European populations we know today were formed from the mixture of these three Caucasoid ancestral components in varying degrees combined with 5,000 years of subsequent continued evolution in different environments with a significant degree of reproductive isolation provided by geographic distance. The phenotypic differences and subracial identities that characterize the modern European populations were already recognizable and described by the authors of antiquity (especially with regard to the Keltic and Germanic peoples), indicating that the continuing process of differentiation was already well-advanced at that time.
The above graphic includes all the hunter-gatherers in one category called “Western European Hunter-Gatherer,” but more precise studies and graphics (see below) differentiate the hunter-gatherer category into four separate groups: Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) in Britain, France and the Iberian peninsula; Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG) in Scandinavia; Eastern Hunter Gatherer (EHG) in eastern Europe; and Caucasus Hunter-Gatherer (CHG) in the Caucasus mountain region. The hunter-gatherers of Scandinavia and eastern Europe were partly descended from Ancient North Eurasians (ANI) and had two genes for light skin pigmentation which the Western Hunter-Gatherers (e.g., “Cheddar Man”) lacked.
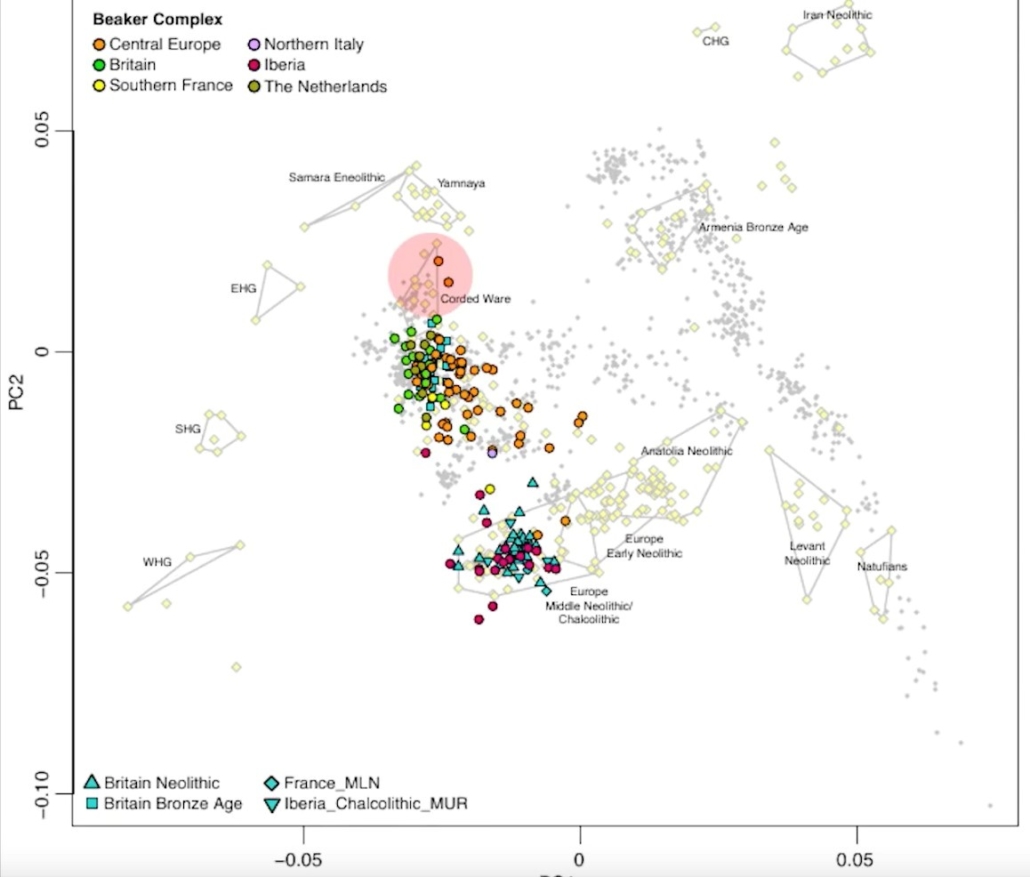
The above diagram (from the video “North Vs South Europe_ Early Neolithic Farmers” on the Survive the Jive channel) provides a visual representation of the genetic relationship between the different ancestral Caucasoid populations in Europe and the Middle East from about 12,000 BC to 2,000 BC, beginning with the first Natufian farmers in the Levant (lower right), which (moving toward the lower center) expanded into Anatolia and then (circa 6,500 BC) into Europe, where the farmers largely replaced the Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG at lower left), to a lesser extent the Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHG at center left), and to a still lesser extent the Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHG at upper left). In northern Europe this blended population was largely replaced by Indo-European Yamnaya pastoralists (top center) by 2,600 BC, providing the predominant ancestry of the peoples of the Corded Ware culture. By the period of the mature Bell Beaker culture in the Bronze Age circa 2,300-2,000 BC, the populations of central and western Europe (including Britain) were a varied blend of Yamnaya, Hunter-Gatherer and Neolithic farmer elements and have remained so ever since.
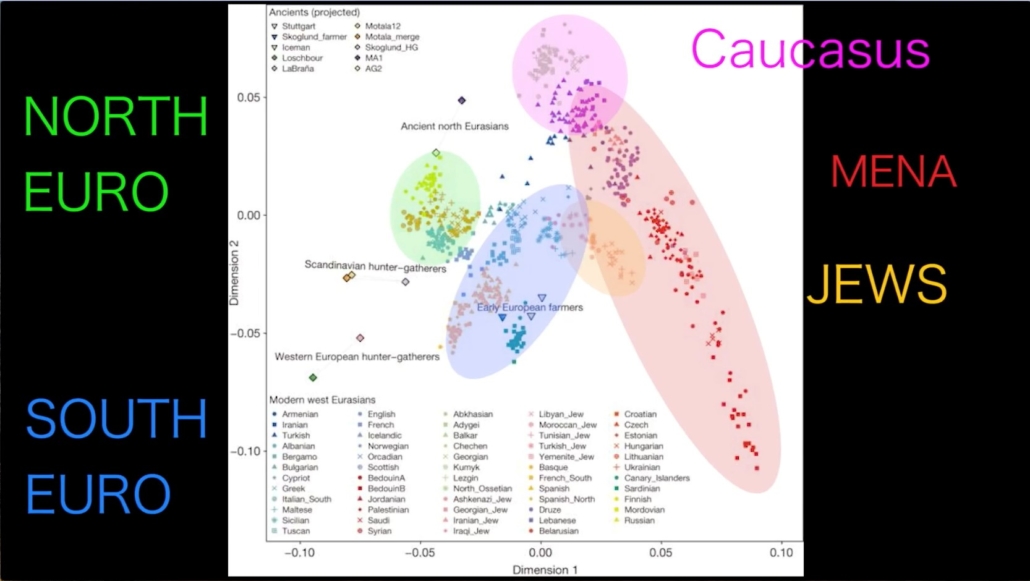
The above diagram of genetic “clusters” (from the same video as the previous diagram) provides a visual representation of the relationship or relative genetic distance between the different modern Caucasoid populations of North Europe (green), South Europe (blue), the Middle East and North Africa or “MENA” (red), the Caucasus region (purple) and the several Jewish components (yellow). The smaller or tighter the cluster, the greater the degree of genetic homogeneity in the category. The Ashkenazi components of the Jewish cluster overlap with the South European cluster, indicating a semi-European ancestry which is consistent with studies indicating the Ashkenazim average 50-60 percent Middle Eastern and 40-50 percent European ancestry. The positions of several ancient populations are also projected onto the diagram, with Ancient North Eurasians (a major component of Yamnaya ancestry) at top center, Scandinavian hunter-gatherers (also largely of Ancient North Eurasian ancestry) at center left, and Western European hunter-gatherers (with no Ancient North Eurasian ancestry) at lower left.
The modern races are often popularly defined and named by skin color, but as this system is based on only one genetic phenotypic difference, when hundreds are involved, it tends to distort the reality of race and racial differences. In the system of modern racial classification outlined below, based on classical phenotypic (non-genetic) physical anthropology, especially Carleton Coon and John Baker, the names assigned to the various subspecies and races are largely derived from geographical locations with which they are associated.
Outline of Modern Human Racial Classification:
SUB-SAHARAN AFRICA GROUP
I. Capoid or Khoisanid Subspecies of southern Africa
A. Khoid (Hottentot) race
B. Sanid (Bushmen) race
II. Congoid Subspecies of sub-Saharan Africa
A. Central Congoid race (Geographic center and origin in the Congo river basin)
1. Palaecongoid subrace (the Congo river basin: Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Congo, Angola)
2. Sudanid subrace (western Africa: Niger, Mali, Senegal, Guinea)
3. Nilotid subrace (southern Sudan; the ancient Nubians were of this subrace)
4. Kafrid or Bantid subrace (east and south Africa: Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, Natal)
B. Bambutid race (African Pygmies)
C. Aethiopid race (Ethiopia, Somalia; hybridized with Caucasoids)
“OUT-OF-AFRICA” GROUP
I. Australoid Subspecies
A. Veddoid race (remnant Australoid population in central and southern India)
B. Negritos (remnants in Malaysia and the Philippines)
C. Melanesian race (New Guinea, Papua, Solomon Islands)
D. Australian-Tasmanian race (Australian Aborigines)
II. Mongoloid Subspecies
A. Northern Mongoloid racial group
1. Northeast Asian race (various subraces in northern China, Manchuria, Korea and Japan)
2. Ainuid race (remnants of aboriginal population in northern Japan)
3. Tungid race (Mongolia and Siberia, Eskimos)
4. Amerindian race (American Indians; originated in eastern Siberia through a circa two-thirds proto-Mongoloid and one-third Ancient North Eurasian Caucasoid mixture; various subraces in North, Central and South America; in some systems considered a separate major racial category or subspecies)
B. Southern Mongoloid racial group
1. Southeast Asian race (various subraces in southern China, Indochina, Thailand, Myanmar [Burma], Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines, the last four partly hybridized with Australoids)
2. Micronesian-Polynesian race (predominantly Southern Mongoloid partly hybridized with Australoids)
III. Caucasoid Subspecies
A. Dravidic race (India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka [Ceylon]; ancient stabilized Indic-Veddoid [Australoid] blend)
B. Turanid race (predominant element in Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, where it has hybridized with
Mongoloids; common in Hungary and Turkey)
C. Indic or Nordindid race (Pakistan and northern India)
D. Irano-Afghan race (predominant in Iran and Afghanistan, primary element in Iraq, common [25%] in Turkey)
E. Armenid race (predominant element in Armenia and Azerbaijan, common in Syria, Lebanon and northern Iraq, primary element among the Ashkenazic Jews)
F. Mediterranid racial group
1. Orientalid or Arabid subrace (predominant in Arabia, major element from Egypt to Syria, primary in northern Sudan, important in Iraq, predominant element among the Oriental Jews)
2. South Mediterranean or Saharid subrace (predominant in Algeria and Libya, important in Morocco, Tunisia and Egypt, primary element among the Sephardic Jews, common element in southern Spain, Sicily and southern Italy, minor in Greece)
-
- East Mediterranean or Pontid subrace (predominant in Greece and the Aegean coast of Turkey, common on the coast of Ukraine, Romania and Bulgaria)
-
- Dinaricized Mediterraneans (Residual mixed types resulting from the blending of Mediterranids with Dinarics, Alpines or Armenids; not a unified type, has much regional variation; predominant element [over 60%] in Sicily and southern Italy, principal element in Turkey [35%], important element in western Syria, Lebanon and central Italy, common in southern France, northern Italy and Greece.)
5. West Mediterranean or Iberid subrace (predominant in Spain, Portugal, Corsica and Sardinia; common in Sicily and coastal areas of Morocco and Tunisia)
G. Ladogan racial group (named after Lake Ladoga; indigenous to Russia where it is an important element; includes Lappish subrace of arctic Europe)
H. Dinaric racial group (predominant in Balkans [Dinaric Mountains] and northern Italy, important in the Czech Republic, eastern and southern Switzerland, western Austria and eastern Ukraine, common in France. Its distribution in Europe, and that of its derived Dinaricized Mediterranean type, may be associated with the expansion of the Neolithic Anatolian farmers beginning circa 6,500 B.C.)
I. Alpine racial group (primary in the Czech Republic [Bohemia] and France, important in eastern and southern Switzerland, Bavaria, Austria and Hungary)
J. Nordish or Northern European racial group (various subraces and subtypes comprising the populations of the British Isles, Scandinavia, and the Netherlands; predominant in Belgium, Germany, Switzerland, Poland, Finland and the Baltic States; majority in Austria, Russia and Ukraine; important in France, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary, common in northern Italy, northern Spain and northern Balkans)
1. Hallstatt Nordic (predominant element in Sweden and southeastern Norway, common in Denmark, western Finland, eastern England and northern Germany)
2. Keltic Nordic (predominant element in Flanders, majority in the Netherlands and northern and western Switzerland, primary element in England, Wales, Ireland, eastern Scotland and the old Frankish country in southwest Germany; ancient Franks and northern Kelts [the Germanokelten] were of this type; probably came to the British Isles with the Bell Beaker culture along with an Indo-European language [e.g., proto-Keltic])
3. Fälish, Dalofalid or Dalo-Nordic type (names from Fälen [German for “plain”] and Dalarna region of Sweden [Kopparberg]; primary element in Denmark, northern Germany, southern Norway, southwest Sweden and Swedish province of Kopparberg)
4. Anglo-Saxon or Old Germanic Reihengräber type (predominant element in the Dutch province of Friesland (Frisia) and the Dutch and German Frisian Islands, important in southeast England and northwest Germany)
5. Trønder type (predominant element in western Norway [whence the name] and Iceland, common in northeast England and Scotland)
6. Borreby type (named after Danish island site; important element in Denmark, southwest coast of Sweden, northern Germany, the Rhineland and the Ruhr)
7. Brünn type (named after Brünn or Brno site, now in the Czech Republic; primary element in western Ireland, common in southwest Norway)
8. East Baltic type (majority element in Finland and the Baltic States, formerly predominant in Old Prussia, but this element now dispersed throughout Germany as a result of the post-war expulsion of the Prussian population from its ancestral homeland)
9. Nordic or Sub-Nordic type (principal element in northern France, important in central Germany and Austria, common in Transylvania and western Ukraine, minor in British Isles)
10. Neo-Danubian type (majority element in Poland and Belorussia, primary in west Ukraine and northwest Russia, important in Hungary, Finland and the Baltic States)
Dominant or predominant = over 60% majority
Majority or major = 50-60% majority
Principal or primary = 25-49% plurality; less than a majority, but most numerous racial type
Important = 25-49% minority; not most numerous racial type
Common = 6-25% minority
Minor = 5% or less minority
The diverse races of the human species outlined above all have their own geographical territory that has historically been exclusively their own, which may be referred to as their racial homeland and is closely identified with the race that inhabits it. Between most of these exclusive homelands are clinal zones — areas of contact between different racial territories. These racial borderlands are frequently areas of interracial contact and intermixture where adjacent races merge into one another, creating racially mixed or hybridized populations of intermediate type called racial clines. The Dravidic race of India, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, created by the intermixture of the local Caucasoid (Indic or Nordindid) and Australoid (Veddoid) populations, and the Aethiopid race of Ethiopia and Somalia, created by the intermixture of the local Caucasoid (Mediterranid) and Congoid races, are two very ancient racial clines which have stabilized into distinct races of intermediate type. Racial clines of more recent formation, where the racial blends are not yet stabilized, include the populations of many Latin American and Caribbean countries, which were created over the last 500 years by the intermixture of various Caucasoid (mostly Mediterranid), Congoid and Amerindian elements. The population of Mexico, for example, is about 5% Caucasoid, 30% Amerindian and 65% Mestizo, the Spanish term for persons of mixed Amerindian-Caucasoid ancestry. (The same term is used in the Philippines for persons of mixed Filipino-Caucasoid ancestry.) The multiracialization of the populations of North America and, more recently, Europe, has begun to transform them into racial clines. As discussed in other essays on this site, this process of racial transformation will eventually cause the effective extinction or nonexistence of the European racial types in the affected areas unless adequate preservationist measures are taken to prevent it.





The late (redacted) David Rockefeller was obsessed with race mixing. He used to send his friends to foreign countries to force them to become multiracial.
He tried 3 times with Japan,unsuccsssfully.
The Americans forced the British to accept Windians in the late 1940’s
Unfortunately, the Yankees will destroy Europe.
If you were related to one of the families that own the Bank of England (although disowned) you would know these things.
I was told by a useful peasant the family used that the Bank of England funded Lenin. Stalin used to live in London. Was he funded by the Bank of England as well?
I was told that in the real World I am not called a peasant. I replied that I feel like one.
I have always had difficulty with the “Out of Africa” theory. Putting aside Denisovians, whose modern day ancestors are Australian Aborigines, and possess the world’s “oldest” DNA, it has been long documented, that no known African has Neanderthal DNA. If so, where did the Neanderthal DNA come from? On top of that, in the Westward expansion of the US from the late 18th century on, the “newcomers” were clearing the land, uncovering graves of giants, many having double rows of teeth. After the Smithsonian Institute was formed in 1846, local newspapers reported that the giant skeletons had been shipped to the Smithsonian. Only recently has the Smithsonian acknowledged that it had received specimens that it had previously denied it had. What has happened to them is still in question.
Approximately three years ago, Human remains were found in Bulgaria and Greece that predate any African site. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/2017/05/22/europe-birthplace-mankind-not-africa-scientists-find/
My point in all of this is simply that the much maligned James Watson stated that virtually nothing is known about how the combinations of DNA affect animals. It is true that chimpanzees share 99% of our DNA, but other animals, even chickens, share 99% of chimpanzee DNA. This reminds me of Eran Elhaik’s 2013 study on Jewish DNA, that was viciously attacked from all sides, due to his criticism of previous studies. The criticism was that other studies took the dart and drew a dart board around it, whereas his study plotted the darts on a dartboard. Every study of ancient human movement has had the dartboard drawn around the dart. Kennewick man is explained away as being Siberian. The fact that Clovis spearheads are found in higher numbers and sites from the Northwest toward the Southeast US, still makes them Siberian. The red headed mummies in Spirit Cave are Siberian, even though no Siberians have red hair. Mesa Verde was built by “Indians”, even though there is no history of Indians building such structures, and so it goes.
There is so much we don’t know, and I suspect, a lot we won’t be allowed to know, about human pre-history.
In the science of archaeology many findings are only released to the public if they fit the current political and social paradigm. We should be very skeptical of finds of ‘giants’, but there are many genuinely perplexing finds discovered in the 19th and early 20th centuries that require proper explanation, but are ‘shoved under the carpet’. Some of these archaeological ‘anomalies’ are covered in “Forbidden Archaeology” by Cremo and Thompson.
Also the Dutch missionary H Verhoffen while stationed on the Indonesian island of Flores during the 1950s to early 60s became a skilled amateur archaeologist and discovered stone implements in sediments at least 500,000 years old. He proposed these rough stone ‘tools’ were produced by what we now call Homo Erectus. These findings would support a valid ‘Out of Asia’ hypothesis.
The Jews need to move quickly to establish their world dictatorship so that the science that undermines their fables and narratives can be suppressed.
What could be when negroes haven’t eaten for a long time:
https://tinyurl.com/ckruyal
Dear friends
Let us cut through the BS.
Tonight I went to the shops late(Which I try to avoid) to be confronted by an African, he said ” ” I said NO.
I went into the shop to buy some goods-The Negro would not take NO for an answer and also a hand(Talk to the hand) in the face. I went to the till at which point the Black appeared, having stealthed me…
”Buy me water” the nig demanded… thinking in that Primate way that intimidation would work–”not with me you Kaffir”. I told him to Go…(and also showed him my club/walking stick) Had I within reasonable rights smashed him in the lip(Go for the biggest body mass){Hackney Police shot a similar Black in 2001-the marksman were told to shoot at the biggest body mass-they chose the BigLips-And were successful} I can provide full details if needed.so not a racial comment just a bio-fact(The big Lip)–The police shot the [redacted] in the lip and dropped him. Job Done.
Anyway, it just shows the Negro arrogance–we should be able to shoot this trash
Had I shown any weakness the Groid would have demanded more.
We in the UK should have Guns to Blast such shite. I am sure the mods will not pass this, but hey I take full responsibility for my wish to stop this blatant intimidation by Black Trash …I write at 4.00am in London, pissed at Black scum who feel free to ”Target white ppl” and they do-and when pulled by LE they whinge and whine.—Straight from the heart, live from London.
The Guardian newspaper’s elite-educated journalists are ahead of this curve.
In a moving review of english writer Angela Siani’s impassioned new book Superior: The Return of Race Science
https://www.theguardian.com/books/2019/may/27/superior-the-return-of-race-science-by-angela-saini-book-review
her fellow briton Alok Jha explains that the concept of race, abolished by UNESCO in 1950, is merely a typical device of ‘whiteness’: a pretext to enable imperialism and white supremacy.
Siani likens this bogus race science to a toxic plant at the heart of white dominated academia and demands it be uprooted. In a moving final passage, exhibiting typical Anglo-Saxon diffidence at sharing intimate family details in published writings, she dilates upon her beloved young son, longing that he may grow to adulthood in a world free of the scourge of white racial pseudoscience.
Regardless of any hoary old matings of cavemen we are all one now and, as Greta Thunberg has demonstrated, the real challenge is saving the Planet together. Siani’s book is a vital antidote to the racial obsession that sadly permeates the crania of too many white men in positions of influence: it would be good to see this site take note of her work by reviewing it here.
Vehmgericht: “Siani’s book is a vital antidote to the racial obsession that sadly permeates the crania of too many white men in positions of influence: it would be good to see this site take note of her work by reviewing it here.”
You’re being sarcastic, right?
Yes I was, but I would love to see Siani’s book dissected here.
Despite being a social history of the reception of the idea of race it was taken as hard scientific fact and praised to the skies in the usual places.
It needs to be communicated to the reading public that books such as Siani’s are light on evidence or just plain wrong, and definitely not the last word!
Very strange this article makes no mention of the Cromagnon man, who are the real “modern humans”, not Africans.
Ignoring the fact that evolution is a pile of jew croc
…and puts the megalithic builders (whomever they were) right in their conventional, wholly unconvincing position on the timeline, as though everything is neatly explained: we’re all essentially still slightly mutated ‘apes’ from nigg… from negroid land, just like our friendly, iconoclastic fellow ‘White’ Doktorb Kikestein tells us.
I’m sorry but there is obviously much more going on, and far more mystery involved with prehistory and human races etc. than is sketched (in antiquated academic strokes) here.
The out of Africa theory has been debunked:
“We have found that a great diversity of Y chromosomal haplotypes in Africa is a result of the mixing of several very distant lineages, some of them not necessarily African, and that Europeiods (at least) do not contain “African” SNPs (those of haplogroups A or B). These important findings put a proverbial dent in the “Out of Africa” theory.”
Klyosov, A. & Rozhanskii, I. (2012); Re-examining the Out of Africa Theory and the Origin of Europeoids (Caucasoids) in Light of DNA Genealogy. Advances in Anthropology, 2, 80-86.
“Which came first? The chicken or the egg?” It doesn’t matter whether the subject is physics, biology or theology. We have no satisfactory accounts of “the beginning” in any of these fields. The Big Bang Theory tells us that everything — space, time, matter, energy — sprang out of literally nothing some 14 billion years ago. But nothing logically cannot contain something, so that explanation fails. We are told that the universe is finite in space — there is nothing beyond its outer edge. Again, we have the problem of nothing containing something. .Evolution tells us that we evolved from apes. But there is no evidence to confirm the transition from ape to man. The “missing link” is still missing. And I guess the “ape theory” is responsible for the claim that humans must have first appeared in Africa — the continent of apes. It is really quite stupid.
The “out of Africa” theory also serves the ideological function of denying the significance of racial differences — we were all originally “the same”. And we all have “the same potential”.
This is not science, it is ideology. If we want to talk about origins when it comes to human beings, we should start with what we see now — the different races — and go no farther back than the artistic, anthropological, archaeological, DNA and other scientific evidence allow us to go.
We can confidently say that race is intimately connected to geography — whites from the far north, blacks from sub-Saharan Africa, Asians from East Asia, and various mixtures of black, white and Asian in other parts of the world. .Native Americans appear to be half-Asian and half-white. Most Latinos appear to be half Native American and half white.
People in the Middle East appear to be a mixture of Asian, white and black — which makes sense, since the Middle East is the crossroads for Europe, Asia and Africa. The people of South-Central Asia (e.g., India, Afghanistan) appear to be a mix of Asian and white.
The Jews are a highly ethnocentric and inbred group that combines Turkic and Mongol elements with white European elements (Ashkenazim) or Moorish elements (a mix of Asian, black and white) with white European elements.
Whites themselves can be subdivided into various groups — Celtic, Anglo-Saxon, Nordic, Germanic, Alpine, Mediterranean, Dinaric, etc.
The cultural achievements of the different races show that they have distinct talents and capabilities. White Europeans created most of what we call “civilization”, including its highest achievements. They have demonstrated the broadest range of capabilities — artistic, intellectual, athletic, military, etc. — and have built great civilizations — Greece, Rome, etc. — that only failed because the Aryan whites who founded them mixed their seed with other races. .