Recent research on Individualism/Collectivism
In cross-cultural perspective, the unique thing about European culture is the tendency for individualism. Individualism is the basis for Western modernization — for why the West has dominated the rest of the world. It is intimately linked with a suite of traits, including democratic and republic forms of government, relatively high status for women, relatively low ethnocentrism, moral universalism, and science.
Research on Individualism/Collectivism has become a rather large academic industry. Recent research has found genetic differences between individualist and collectivist societies and has linked this dimension to economic growth and innovation. Several of these strands come together in a paper by Yuriy Gorodnichenko and Gérard Roland, “Culture, Institutions, and the Wealth of Nations” put out by the Center for Economic Policy Research (short online version: “Does Culture Affect Long-run Growth.”)
The long version of the article notes that individualism/collectivism is “the main dimension of cultural variation.”
Individualism emphasizes personal freedom and achievement. Individualist culture therefore awards social status to personal accomplishments such as important discoveries, innovations or great artistic achievements. On the other hand, individualism can make collective action more difficult because individuals pursue their own interest without internalizing collective interests. Collectivism makes collective action easier in the sense that individuals internalize group interests to a greater degree. However, it also encourages conformity and discourages individuals from standing out. This framework implies that individualism should encourage innovation, everything else equal, but collectivism should have an advantage in coordinating production processes and in various forms of collective action.
Their model relies on the idea that collectivist cultures are better at producing goods but that individualist cultures are better at creating innovations required for new products. Individualist cultures are therefore proposed to be better at producing growth, but not as good for efficiently producing goods once the technology is in place. In support, they note several anecdotal examples where technological innovations originating in Western societies led to products that were produced more efficiently in Japan. As another example, they note that General Motors was unable to introduce the Toyota culture based on teamwork and consensus into the United States.
This figure in the upper left below shows world-wide variation in individualism-collectivism ranging from yellow (individualist) to red (collectivist).
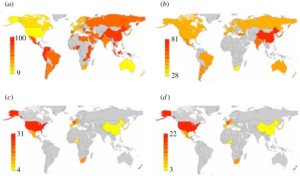
Geographical coincidence between serotonin transporter gene diversity and cultural traits of individualism–collectivism across countries. Gray areas indicate geographical regions where no published data are available. (a) Map of frequency distribution of Individualism-Collectivism. (b) Map of frequency distribution of S alleles of 5-HTTLPR. (c) Map of frequency of global prevalence of anxiety. (d) Map of frequency of global prevalence of mood disorders. Yellow to red colour bar indicates low to high prevalence. From Chiao and Blizinsky (2009).
Notice anything? Quite clearly, individualism is a European phenomenon.
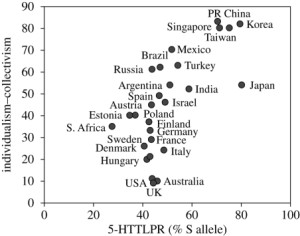
Gorodnichenko and Rolandin essentially measure Europeanness genetically, using Cavalli-Sforza’s (1994) data on genetic distance based on blood groups and corrected for the percentage of an ethnic group in country. Although the authors see the genetic data as mere proxies for the cultural differences, needless to say, they are also proxies for underlying genetic differences between these culture regions that go well beyond genes for blood type. By their measures, the US is the most individualistic country in the world, so that the closer countries are genetically to the US, the more individualistic they are. This is a strong correlation: “The strong negative correlation between genetic distance (computed relative to USA, which has a highly individualistic culture) and individualism suggest that genetic distance may be a strong instrument.”
The article also plugs into recent research indicating a genetic basis for individualism/collectivism. Collectivist cultures are associated with two genetic markers both of which make people more prone to stress in the absence of the kind of social support found in collectivist cultures. Chiao and Blizinsky (2009) found a strong correlation between collectivism and the presence of a short (S) allele in the polymorphism 5-HTTLPR of the serotonin transporter gene SLC6A4 in 30 countries. This allele is known to put individuals at greater risk for depression when exposed to life stressors. The idea is that that collectivist cultures protect individuals from these risks by embedding them more strongly in communities with strong social links thus providing strong psychological support networks. Therefore the gene is more adaptive in collectivist cultures and probably selected against in individualist cultures.
Here’s another figure from Chiao and Blizinsky (2009) again showing the rank order of cultures on individualism-collectivism but also showing the correlation with the percentage of the 5-HTTLPR allele.
Another (compatible) explanation is that people with the short form of the allele are more sensitive to social disapproval, as found in a recent paper by Thomason et al. People with the short form of the allele reacted more strongly to frowning faces — not a good trait if one is adopting non-conformist positions. It’s a gene that those of us subjected to public opprobrium for politically incorrect views would do well to be without.
Another genetic marker for collectivism is the G allele in polymorphism A118G in the μ-opioid receptor gene that leads to higher stress in case of social rejection.Way and Liebermann (2010) reason that this gene and the other genes linked thus far to individualism/collectivism operate by making people more socially sensitive. This in turn makes them more prone to depression in the absence of the strong social support available in collectivist cultures. For example, adults who have had a serious personal loss have less activation in the μ-opioid system, suggesting that it is sensitive to social inclusion. They also point to a genetic variant in the monoamine oxidase system that is activated under conditions of social exclusion, although to date this gene has not been correlated with individualism/collectivism.
Relying on a paper by Fincher et al., Chiao and Blizinsky propose that ultimately worldwide differences in genes for individualism/collectivism were favored by natural selection because collectivism is better for combating pathogens such as infectious diseases and parasites. The basic idea is that collectivist cultures would be less open to new people and hence less likely to be infected; retaining the status quo is adaptive because change may allow diseases and parasites to enter the culture.
However, it should be noted that Fincher et al. simply find a correlation between pathogen presence and collectivism. Their proposal for why such a correlation should occur is not based on any data. The authors note that the basic correlation is with latitude: Warmer climates have fewer pathogens and are more likely to be collectivistic. This correlation is also compatible with my argument that the European tendency toward individualism is the result of lessened importance of group-based competition during the Ice Ages for the ancestors of Europeans because large kinship-based groups would not have been supported because of the ecological constraints imposed by a cold climate. Indeed, the explanation of collectivism as involving its utility in group-based competition has far more surface plausibility than an explanation based on the putative benefits of collectivism for avoiding pathogens.
Although not included in the Gorodnichenko and Roland study, another gene linked to non-conformity is the 7R allele of the D4 dopamine receptor gene associated with novelty seeking, impulsivity, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. This allele is absent in China, although alleles derived from the 7R allele are common. Cochran and Harpending (2009, p. 112) suggest that this pattern may be due to high levels of social controls weeding out non-conforming individuals. “The Japanese say that the nail that sticks out is hammered down, but in China it may have been pulled out and thrown away.”
This scenario of actively suppressing non-conformists does not fit well with the pathogen prevention explanation of non-conformity but fits well with the importance of getting rid of such a gene in the interests of promoting cohesive groups. Similarly, I have argued that there was strong selection for social conformity within traditional Jewish communities. People who were less ethnocentric were ultimately excluded from the gene pool.
In any case, getting back to the Gorodnichenko and Roland paper, innovation was measured by the number of patents per million of population. The figure below shows a strong correlation.
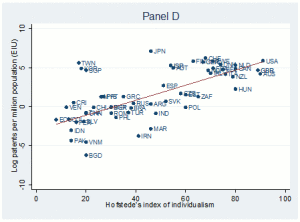
Individualism versus Patents per Million Population
However, G&R do not correct their results for IQ — a rather amazing omission considering that Richard Lynn and Tatu Vanhanen’s IQ and the Wealth of Nations (2002) found strong associations between economic development and measures of average national IQ. Notice in the figure that Japan with a high average IQ has the highest level of patents as measured by G & R but they score in the middle on individualism/collectivism. Israel is another society that, compared to Western norms, is relatively collectivist (~60 on Hofstede’s index) but relatively high on patents. We may anticipate that as China continues its spectacular development, they will also have increasing numbers of patents per capita, given its huge commitment to education in basic science and engineering.
On the other hand, it has often been noted that because of the increasing dominance in the West of the financial sector, smart people are increasingly going into investment banking rather than engineering and basic science. Unlike engineering and basic science, the financial sector does not contribute to growth or innovation. Indeed, the recent financial collapse resulting from malfeasance in the financial sector shows that this sector is quite capable of having a negative effect on economic growth.
Moreover, because of free trade policies, individualist cultures are prone to exporting jobs to collectivist cultures with a strong sense that economic policy should be designed in the national interest. As a result of an unholy alliance between ethnic lobbies and business interests, individualist cultures are also prone to massive immigration of both skilled and especially low-IQ unskilled labor without regard for effects on national cohesiveness or any other costs.
European-derived cultures are committed to multiculturalism, and they are being swamped by economic refugees from collectivist cultures, dispossessing their founding peoples. In the long run, in the absence of a political revolution against non-European immigration, it is highly doubtful that individualist cultures can survive. The research reviewed here indicates that predispositions to individualism/collectivism are genetically based. The biological basis of individualism/collectivism combined with an official ideology of multiculturalism means that people prone to collectivism will likely continue their collectivist ways even as citizens of individualist cultures. Certainly the lack of integration of Muslims in Western societies is a prime example of lack of integration. And, although Jews have certainly assimilated in many ways, they retain strong ties to other Jewish communities and they are highly organized in opposition to the interests of Europeans. As noted elsewhere, Jews would not matter except that they have a strong sense of fear and loathing of erstwhile European majorities. Jews are particularly important because of their elite status in terms of wealth as well as their influence on the media and on the political process.
As non-Europeans become the majority in traditionally European societies, there is no reason to suppose that they will retain individualist political and cultural institutions. As they say, demography is destiny.
Kevin MacDonald is editor of The Occidental Observer and a professor of psychology at California State University–Long Beach. Email him.





